On April 27, a research paper entitled "data driven capacity estimation of commercial lithium-ion batteries from voltage relaxation" was published online in nature COMMUNICATIONS. The research was completed by Professor WEI Xuezhe’s research team, School of Automotive Studies, Tongji University. ZHU Jiangong, an Associate Professor was the first author of the paper while Professor Dai Haifeng the corresponding author. The authors are from Tongji University and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany. This research result provides a new approach to power battery capacity estimation, and provides new ideas for technical development of power system in various application scenarios.

Paper published in nature COMMUNICATIONS entitled Data-driven capacity estimation of commercial lithium-ion batteries from voltage relaxation
The capacity of the battery decreases gradually when in use. For example, as far as the whole electric vehicle is concerned, the battery capacity determines the maximum driving range of the vehicle after charging. For the battery system, battery capacity is not only the necessary input of many key states in battery management, but also an important indicator of battery health. However, when a vehicle is in operation, the battery capacity is difficult to obtain.
A capacity estimation method based on the characteristics of battery relaxation voltage is proposed Driven with the help of a data-driven approach. This approach extracts the parameters from the relaxation voltage information after the power battery is fully charged, and the battery capacity estimation error (RMSE) is 1.1% (Fig. 1). By constructing a transfer learning method, the generalization ability and universality of the estimation method are improved. The constructed transfer learning method is verified on two other batteries with different material systems, and the estimation error is less than 1.7%.
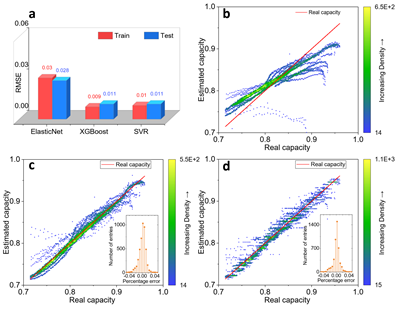
A capacity estimation method based on the characteristics of battery relaxation voltage
The research results reveal the long cycle test data of three commercial lithium-ion power batteries with different material systems (as shown in Table 1), including 130 battery cells. Each cell has been cycled for 50 ~ 1400 times according to different experimental conditions. The experimental conditions include three temperature at 25 ℃, 35 ℃ and 45 ℃ and five charge discharge rates at 0.25c, 0.5c, 1C, 2C and 4C.
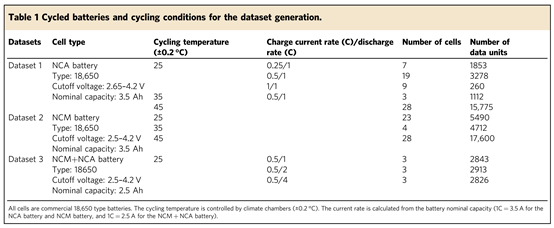
Long cycle test data of commercial lithium-ion power batteries with three different material systems
According to experts in this field, the capacity estimation method based on the parameters of battery relaxation voltage proposed in this research has the advantages of not relying on battery history information and environmental information and not requiring specific battery test conditions and voltage range. It provides new solutions to the development of various application scenarios and power supply technologies of power battery, such as parking and charging, power exchange, echelon service life evaluation and life prediction.
This research was mainly completed by Tongji University, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany and the University of British Columbia. The research was supported by the Humboldt Foundation of Germany, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the special fund for basic scientific research business expenses of central universities, and supported by the electrochemical energy storage platform of Ulm Karlsruhe in Germany.
The researchers keep their data open to the world: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6379165
Link to paper:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29837-w