On August 14, 2019, research achievements of an eight-year state key project entitled “Evolution of the Deep Sea Process in the South China Sea” of National Natural Science Foundation, China’s biggest ever basic research project in marine science, were briefed in Tongji University. More than 10 senior scientists revealed some breakthroughs in science in their plain words.
"We are conducting an experiment. For the first time, we have explained the key outcomes of major basic research programs at the national level in plain words for the academia and the populace. We seek to explain the scientific frontier and introduce our own independent innovations in words that even laypeople can understand.", explained Prof. WANG Pinxian, Director of Advisory Committee of the South China Sea Deep Plan, a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and professor of School of Ocean and Earth Sciences of Tongji University.
This was the first time that the achievements of major basic research programs were made available to the amateurs and laypeople.
"Like dissecting a sparrow, we are trying to reveal the ‘life history' of this marginal sea—the South China Sea from three aspects: the ‘bones', i.e. the formation and evolution of the deep-sea basin; the ‘flesh', i.e. the environmental information contained in the deep-sea sediment; and the 'blood', i.e. the biogeochemical system of the sea water."

"The South China Sea is not an ‘Atlantic in miniature’. The traditional Atlantic type "intraplate rupture" model is forming an open ocean basin through pulling in three directions. The South China Sea is rather squeezed by ‘enemy on three sides’ while the plate-edge basin in the South China Sea had been ‘squeezed, pulled and squeezed’ into a margin ocean basin that ‘does not grow big’ ".
At the briefing, many amateurs at the scene also listened with zest to the vivid expressions through metaphor and intuitive charts made by a host of senior scientists such as WANG Pinxian, LIN Lin, JIAN Zhishi, DAI Minhan and JIAO Nianzhi.
In the eight years since the implementation of the South China Sea Deep Plan, 51 key projects and 9 projects were investigated, attracting more than 700 researchers from 32 organizations all over China. Hundreds of anchor system measurements and offshore tests have been carried out in the deep water area of the South China Sea, a variety of deep geophysical tests have been carried out, 4 ocean drilling voyages and 4 deep submarine voyages have been completed, and a large number of observations and experiments in various disciplines such as biogeochemistry have been carried out, exceeding the scheduled plan. During the stock-taking process of outcomes, 18 highlights were identified. A series of seminars and small-scale international and domestic seminars were subsequently convened in the six months that followed.
The briefing was composed of three sections: reports by team leaders on the three major breakthroughs in tectonic plate rift, low latitude driving in climate, and carbon pump efficiency in modern processes, respectively; briefings on 11 highlights that are accessible to the general public; compilations and posters of 18 aggregated highlights.

"The 11 presentations are made not to show the academic level, but to unfold the projects in a strong story-telling manner. The briefing is not a comprehensive description of the highlights of the research results, but a selection of particularly exciting content". Academician Wang Pinxian said that on this occasion, he wanted to break the traditional habits that the higher the learning, the more boring it is. He proved with examples that the higher the level, the easier to understand the report. He hoped that more people would review the results of eight years of research with interest.
We have achieved a series of major breakthrough research results beyond expectations.
"The South China Sea Deep Plan has exceeded our expectations and made breakthroughs at the academic level. Among the world's many deep-sea basins, the South China Sea has emerged as the most thoroughly investigated marginal sea. It is becoming a natural laboratory for world marine scientific research," Professor WANG said. He added that the implementation of this major plan has achieved new understanding and has become a milestone in deep research in the South China Sea. It has enabled China to master the leading power in scientific research in the South China Sea, formed a multidisciplinary team of deep-sea scientists in China, and established our independent views on major basic scientific issues.
Which of the two sub-basins in the east and west of the South China Sea is older? Where did the South China Sea open? How does deep water flow in the South China Sea? Where did the deep sediments in the South China Sea come from and how are they transported? What are the microorganisms and their roles in the deep water and sediments of the South China Sea? "Back to eight years ago, we didn't know anything about these issues and all we could do was only guess or copy from foreign textbooks." WANG noted.
During the 8-year academic marathon, the team put forward a series of new hypotheses, especially in the aspects of basin origin and climate evolution, which went against traditional wisdom with new hypotheses.
For the origin of the sea basin, the world's standard of research comes from the North Atlantic. Since the 1980s, European and American researchers have believed that the formation process of the South China Sea was a replica of the Atlantic Ocean, just smaller in scale and shorter in age. The current research showed that the South China Sea is not a "small Atlantic Ocean". The South China Sea and the Atlantic Ocean have two fundamentally different ocean basin formation mechanisms. The former is a "plate margin rift" and the latter is an "intraplate rift". Study in the South China Sea points out the mistake of confusing the two in international literature and industry practice, and proposes that the western Pacific marginal sea is a series of "plate marginal rift", which needs to be revisited with new perspectives and technologies.
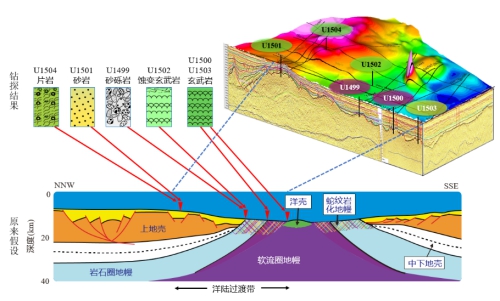
Drilling findings in the South China Sea challenged the traditional assumption by proposing that the basement of the ocean-land transition zone is not serpentine mantle. Below is a schematic diagram of profile interpretation according to the Atlantic model, and at the top left is the basement lithology revealed by drilling.
Another breakthrough is the "low latitude drive" of climate change. The study of climate evolution started with the discovery of the Great Ice Age. Its core is to successfully explain the periodicity of ice cover expansion and contraction in the past million years by using the changes in solar radiation received in high latitudes of the northern hemisphere. The study of the South China Sea put forward the viewpoint of "low latitude drive" of climate evolution, pointing out that the periodicity of driving force is different for the changes in the size of the ice sheet in the high latitude area and the changes in monsoon rainfall in the low latitude area. In other words, the change in the periodicity of precipitation in the low latitude area is not determined by the ice sheet in the high latitude area. In fact, the amount of solar radiation is concentrated in the low latitudes. The low latitudes process is the source of dry and wet climate, drought and flood disasters, but it has not been paid attention to for a long time, and the attention is focused on the high latitudes ice sheet in the northern hemisphere. The study of the South China Sea further shows that the greater change in the low latitude sea area lies not in the surface but in the subsurface water. The orbital cycle has not only a 10,000-year ice age cycle, but also a 400,000-year monsoon climate cycle. The current earth is at a low ebb. Attention should be paid to the long-term prediction of global climate change.
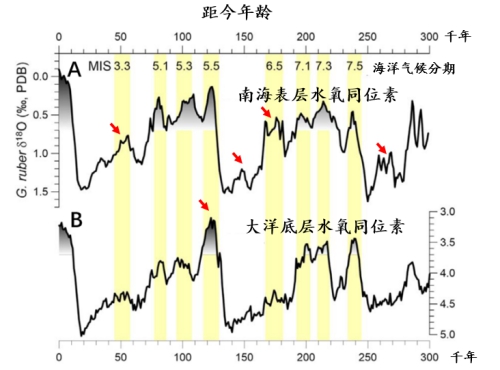
Two types of ocean oxygen isotope curves in recent 300,000 years. A. surface water in the South China Sea; B. ocean bottom water. Red arrows indicate significant differences between the two.
"Based on a large number of field observations and in-situ exploration, the source of some 'universal' knowledge has been traced. According to the characteristics of the western Pacific Ocean and low latitude sea areas, new knowledge unlike that of predecessors has been put forward. However, the current progress can only be said to have raised the problem, which is still a long way from being solved." WANG said that only by further combining the research in the North Atlantic and the West Pacific, and combining the low latitude process with the high latitude process, can the origin and climate evolution of the sea basin be understood thoroughly.
In addition, there are many marginal seas in the world, and it is the first time that systematic observation and research on water and carbon cycle in deep marginal sea basins is concentrated, like the deep plan of the South China Sea. The deep water in the Pacific Ocean enters the South China Sea through the 2,600m-deep Bashi Channel, resulting in a "deep water waterfall" and a three-layer circulation structure in the South China Sea. Through the combination of actual measurement and simulation, a systematic understanding of the interaction between ocean and continental factors has been obtained.
"The progress in the above three aspects has raised the understanding of the depth of the South China Sea to a new level, making it one of the most studied cases in the international marginal seas." Academician Wang said.
Source(in Chinese):https://news.tongji.edu.cn/info/1003/70826.htm